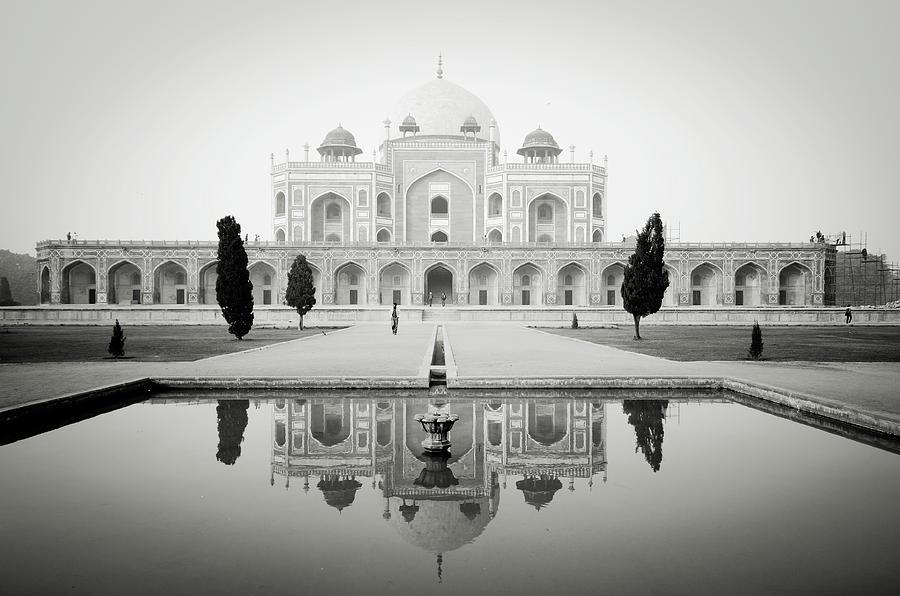
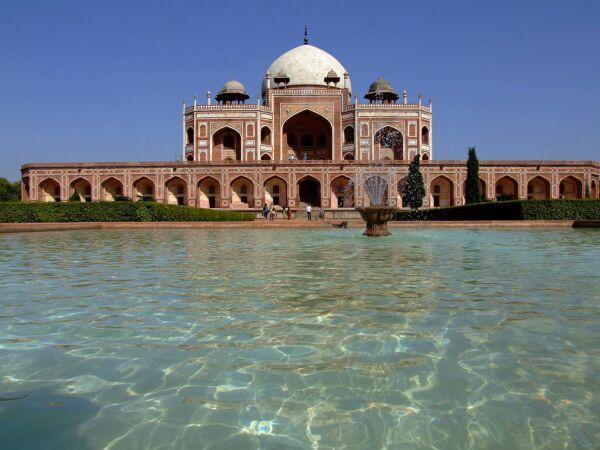
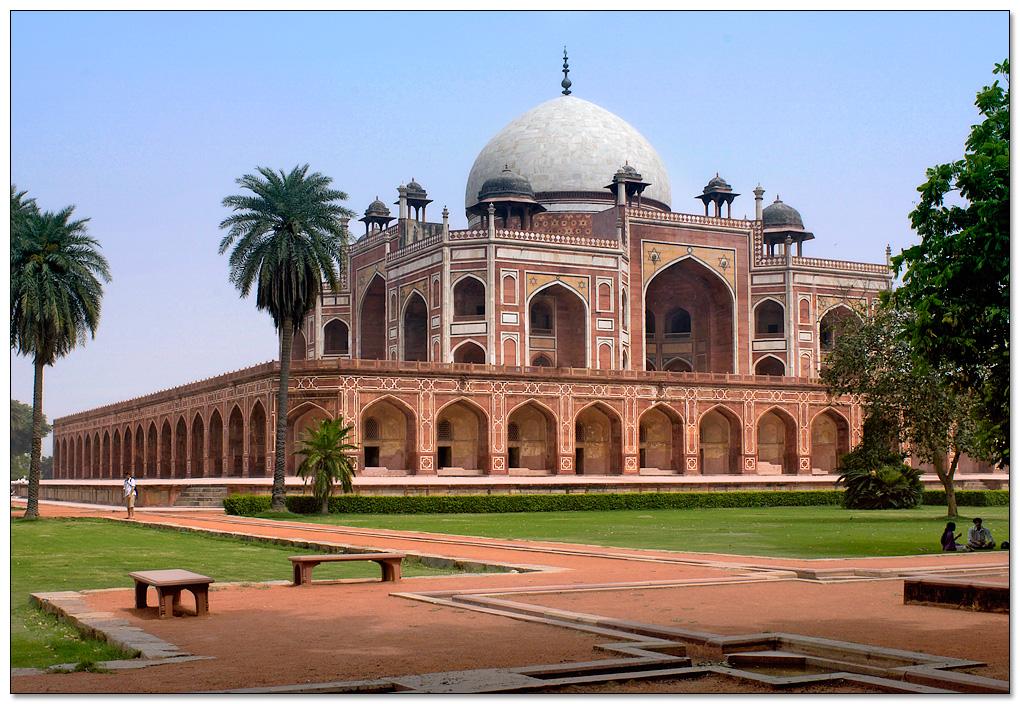
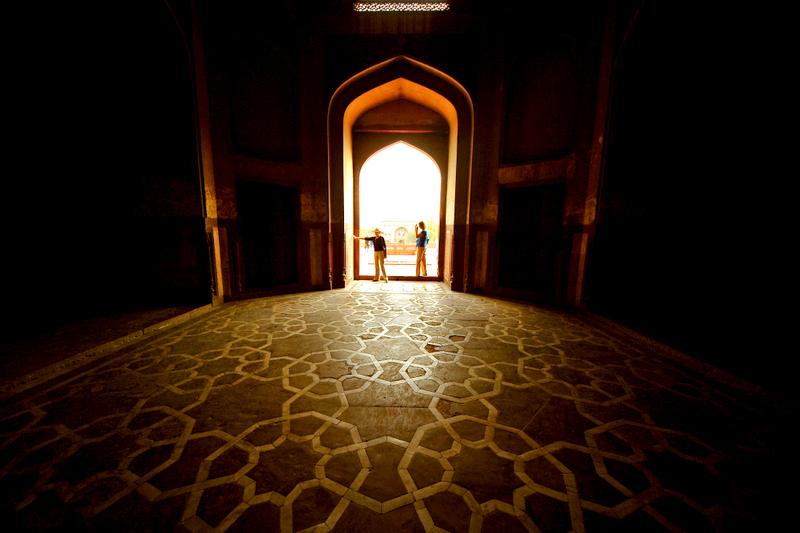
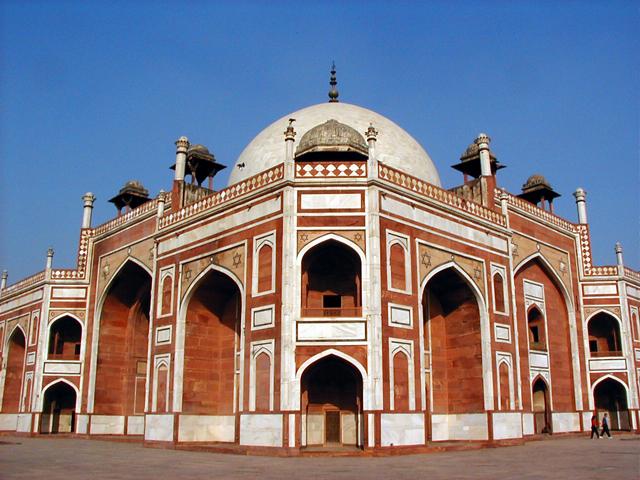
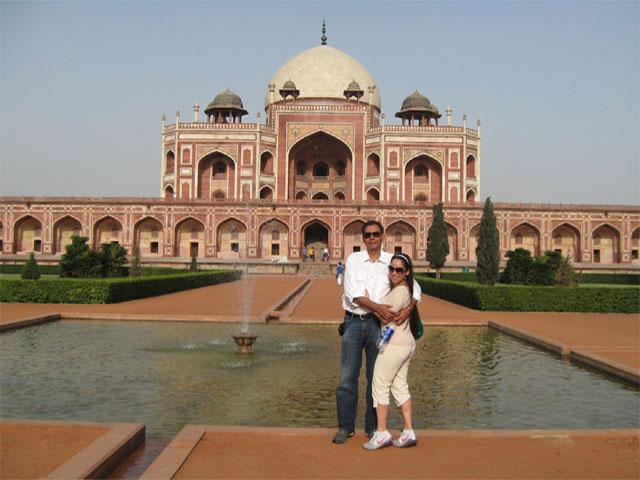
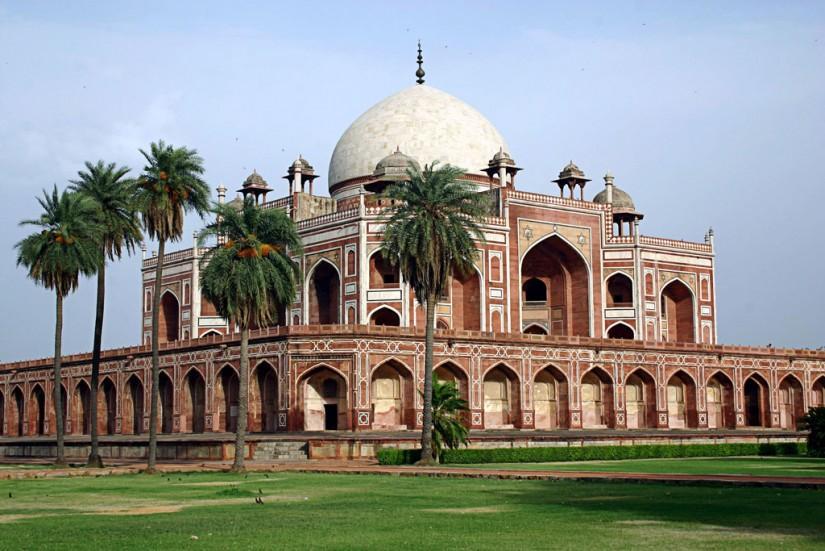
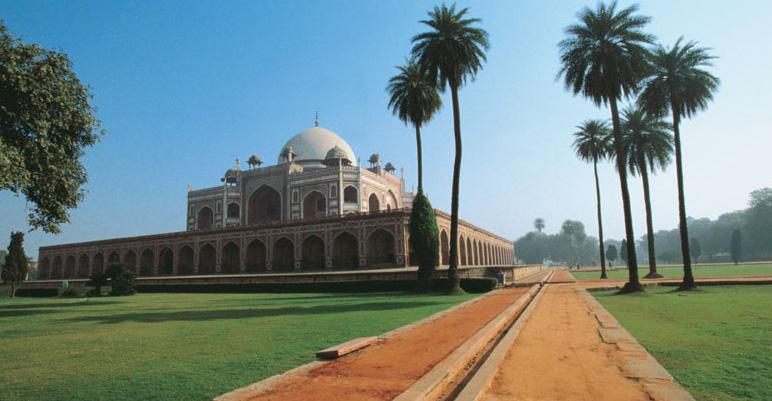
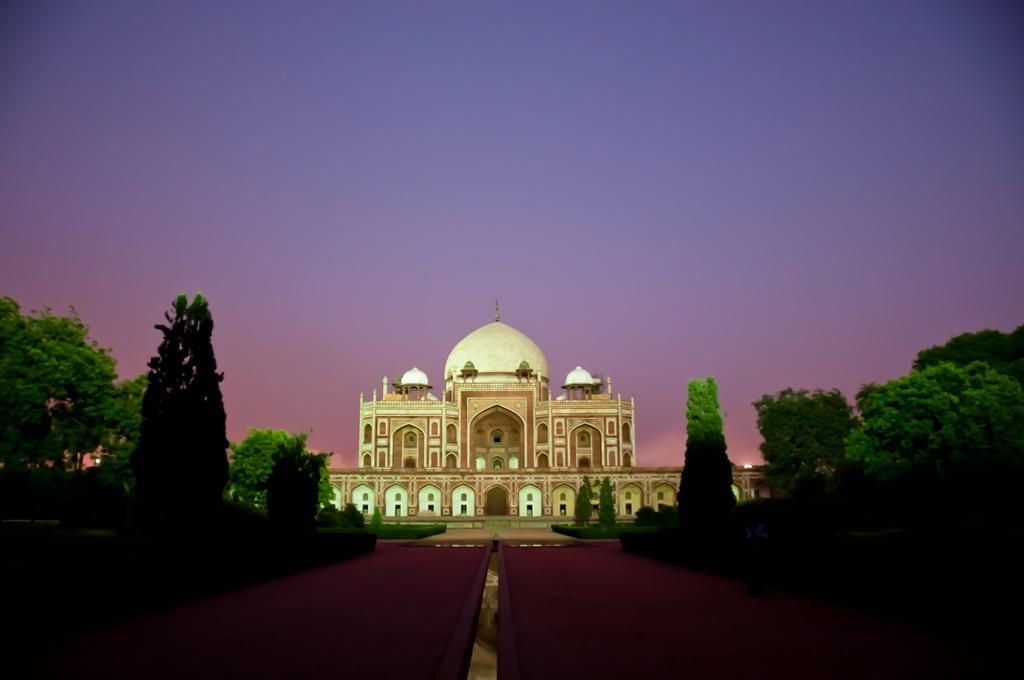
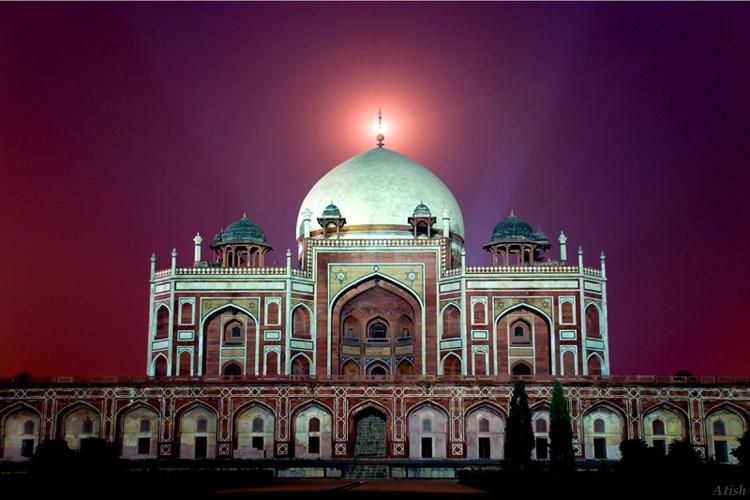
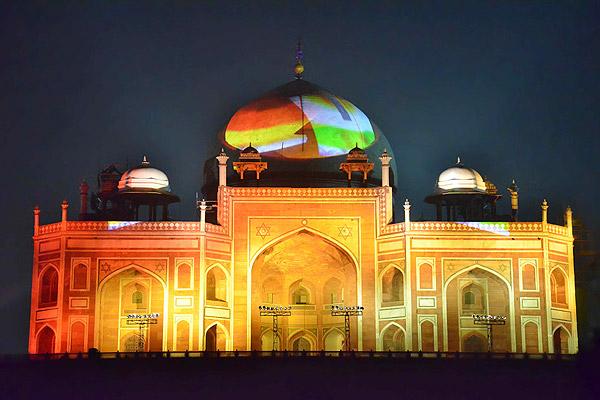













The most perfectly proportioned and captivating of Delhi’s mausoleums, Humayan’s tomb seems to float above the gardens that surround it. Built in the mid-16th century by Haji Begum, the Persian-born senior wife of the Mughal emperor Humayun, the tomb brings together Persian and Mughal elements, creating a template that strongly influenced the Taj Mahal.
Following six years of restoration, completed in 2013, the tomb, other monuments and gardens are looking bright and beautiful. The arched facade is inlaid with bands of white marble and red sandstone, and the building follows strict rules of Islamic geometry, with an emphasis on the number eight. The surrounding gardens are alive with green parakeets and contain the tombs of the emperor’s favourite barber and Haji Begum. This was where the last Mughal emperor, Bahadur Shah Zafar, took refuge before being captured and exiled by the British in 1857.
To the right as you enter the complex, Isa Khan’s tomb is a fine example of Lodi-era architecture, constructed in the 16th century. Further south is the monumental Khan-i-Khanan’s tomb , plundered in Mughal times to build Safdarjang’s tomb.
Built in: 1569
Year of Inscription: 1993
The last refuge of Mughal Emperor Humayun reminds rather of a luxurious palace, than a tomb. Located in the eastern part of Dehli, Humayun’s tomb is one of the best preserved Mughal monuments. This spellbinding mausoleum is the first example of Mughal architecture in India. After a century from its construction Humayun’s tomb inspired the construction of the more famous Taj Mahal.
From the point of view of the history of architecture this building is the unique connecting link between the Gur Emir, where Humayun’s ancestor Tamerlane is buried, and the mausoleum of his grandson Shah Jahan, i.e. Taj Mahal. Humayun’s tomb was built thanks to the initiative of his widow Hamida Banu Begum, who commenced the construction of a mausoleum for her deceased husband in 1565, nine years after his death. The construction was finished in 1572.
The architecture of the tomb is strongly influenced by Persian architecture. The architect of the building Mirak Mirza Ghiyas himself was of Persian origin. Ghiyas constructed the tomb in the center of a Persian-style chaharbagh garden (translated from Farsi - four gardens) with quadrilateral form. The garden, divided in four main parts by walkways or flowing water is created to resemble the paradise garden described in the Quran. These four main parts on their turn are separated by channels to 36 parts.
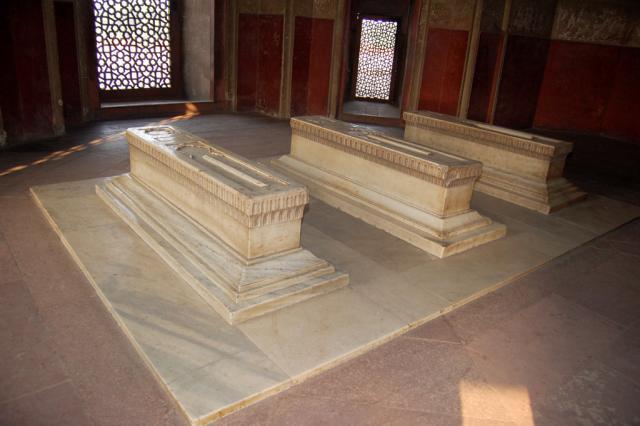
From the 17th to the 19th centuries the garden was gradually filled with the tombs of Humayun’s descendants and his entourage. Several Mughal emperors are even buried inside Humayun’s mausoleum. Humayun’s mausoleum has earned the title of necropolis of the Mughal dynasty. No sepulcher in India or elsewhere contains such a high number of tombs of the Mughal emperors and their relatives. Moreover, Humayun’s tomb is the first garden-tomb on the Indian subcontinent.
The mausoleum stands on a massive platform which has a height of up to 7 meters. The building is constructed from red sandstone, while the tomb itself is made of yellow and black marble. The two-storied mausoleum is crowned with white Persian style marble dome that seems weightless and imponderable. The height of Humayun's Tomb is 47 meters, and its breadth is 91 meters. The lower tier of this rectangular construction is decorated with graceful arches, which are located around the whole perimeter of the building.
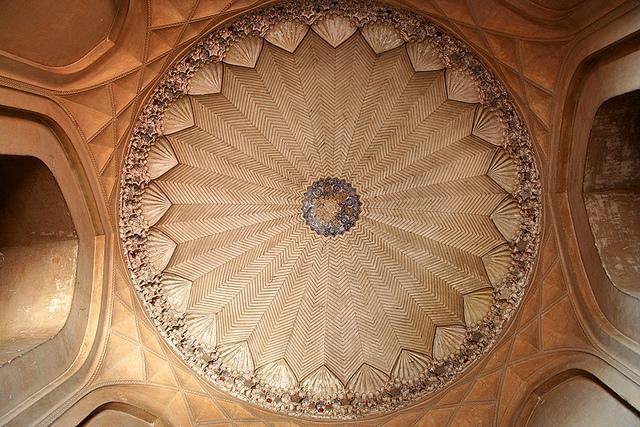
The cenotaph of the ruler is located in the center of the upper tier in a large room decorated with several rows of arched windows. The central chamber is octagonal with corner-chambers which house the graves of other members of the royal family. The real grave of the emperor is on the basement floor.
The architecture of the mausoleum has details both from Persian architecture and Indian architectural traditions. The Persian influence can be seen in the arched alcoves, corridors and the high double dome, while Indian traditions have inspired the creation of the kiosks, which give it a pyramidal outline from distance.
Reasons for Inscription: The reason behind inscribing this wonderful construction relates with the fact that it exemplifies the formative stage of Mughal architecture. The tomb also represents the specimen of the double-domed elevation with kiosks on large scale. The Mughal style of garden tomb was first introduced in this tomb which used to include causeways and channels around it.
Category: Secular structure, burial
An insight into the Humayun's Tomb
After the death of Humayun, his eldest wife Bega Begam took initiative to build this tomb. In 1569, she employed Mirak Mirza Ghiyath, a Persian architect to build this wonderful monument. This red sandstone tomb is built amidst a square garden divided into four main parterres known as charbagh. At the centre of this garden a shallow water-channel can be seen. There are two double-storeyed gateways on the west and south of the monument. The centre of the western wall is occupied by a baradari (pavilion) and a hammam( bathroom) is found at the centre of northern wall.
The mausoleum is set on a high, wide and terraced platform. Across the sides small arched cells add to its architectural importance. It is designed like an asymmetrical octagon with four long and four short sides. A 42.5m high double dome is designed with marble and edged by exclusively carved chhatris (pillared kiosks). The interior is a spacious chamber which is octagonal in shape and set with domed roof compartments. The chamber is again interconnected with galleries and corridors. The entire structure is built with red sand stone with white and black inlaid marble borders.
Are you interested to know more about the mausoleum of Mughal Era?
Let us hear from you at +91 33 4046 4646.
As suggested and to be customized as per request

 Loading..
Loading..